No products in the cart.
Overview of The Nazca History
![]()
The Nazca culture started when the people settled in Ica and the Nazca Valleys in Peru. With time, the effects of their settlement were felt far and wide. However, there’s no evidence that the Nazca community had colonization or military type of expansion, this community only expanded their territory and name through prestige and trade.
The Nazca people had intensive agriculture in an area that has been characterized by unpredictable natural events like, earthquakes, frequent droughts and flash flooding. The need for water played a major role in their lifestyle.
By 500AD, the Nazca civilization started to decline in influence and control. Then by 750AD, this community had completely fallen. One of the most significant contributors to the downfall of the Nazca culture was El Nino. The community succumbed to the wrath of Mother Nature.
Evidence shows that the Nazca people might have led to the accelerated effects of the El Nino through cutting down of trees to give room for growing cotton and maize. These trees, Prosopis pallida, typically play an essential role in reducing soil erosion. Gradual soil erosion due to the destruction of these trees led to climatic calamities such as El Nino. Eventually, the soil became dry and couldn’t hold crops anymore.
PRESERVING Nazca ART
AND CULTURE
WHILE GIVING CHARITABLE
DONATIONS TO OUR SOCIETY
At Nazca Head, we love the idea of preserving the Nazca culture but that’s not our only objective. With each merch you buy from us, 10% is sent to UNESCO’s World Heritage Centre.
We believe that with a little love, ‘we can change the world’.
If there’s one thing, the Nazca people are known for, it is their beautiful art. Their physical appearance, ornaments, and clothing are elements that are easily traced from drawings in their pottery representation. More importantly, this was a community that had a rich culture.
Nazca pottery
Without a doubt, the Nazca pottery designs are instantly recognizable. The ease of identifying this great art is no doubt because of the culture of ‘not writing but drawing’ on the pots. Back then, designs on the jars were a vital form of communication and sharing of ideas between the community. It was also considered as a religious practice.
In most cases, the pots were only used during burial offerings, ritual use, and pure decoration. We all acknowledge the fact that these incredible designs require a lot of practice and skill. Therefore, the potters didn’t just scribble stuff on the body of the pots. It takes years of practice and training to even come close to creating a replica of the designs found on most of these artifacts.
What’s more, the ceramic displays of the Nazca potters were widely spread in ancient civilizations. These pots were hand-made since the Nazca civilization thrived long before the invention of the pottery wheel. But potters did use the turntable just to decorate the pot with intricate designs.
Although the Nazca potters used simple technology, the ceramics featured the most extensive color range and could be marketable in any trade. Some of the distinctive markers in the Nazca pots include the shape of human heads that showed the practice of taking heads as trophies after battles.
Nazca pottery vessels were decorated with vividly rendered patterns, gods, shamans, animals such as monkeys, condors or mythical creatures.
Nazca Textiles
The Nazca community is also known for its mastery in textile creations. Typically, the textiles were designed by women in the community. What’s more, the women were using a backstrap loom. These textiles appear mostly on the pots. However, textiles were woven long before they started to appear on pottery. And thankfully, the desert preserved most of the textiles of the Nazca culture, which is why we know so much about their original designs today.
At Cahauchi, researchers were able to recover shawls, belts, tunics, and other items from burial sites. Most of the bodies found in those gravesites were wrapped in textiles, which was a part of the burial traditions.
In addition, these textiles can also be found in some of the partial burials as well. The textiles tell a lot about Nazca history. For instance, the materials used to create the textiles show that women had access to high-end materials.
Figures were popular in designs, most often are depicted participating in harvesting scenes. Animal depictions, similar to those in the geoglyphs and pottery designs, were also a popular subject.
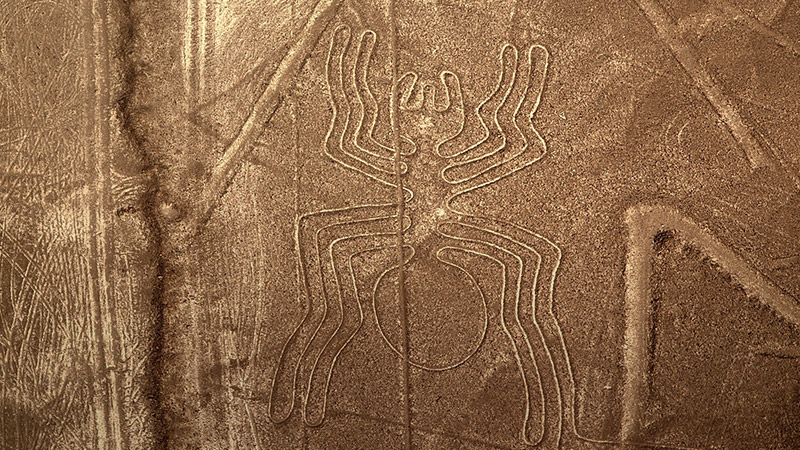
Nazca Lines
If you haven’t noticed this by now, the Nazca people drew lots of geoglyphs across the desert, showing the location of water sources. Sometimes, these lines indicated animal grazing sites, humans, or even plants within the vicinity of their community. But to this very day, the exact use of the Nazca lines is still disputed by many researchers, and the most widely recognized theory is that “the Nazca lines were used as a path to processions and religious rites.”
Researchers have demonstrated techniques to show the potential ways how this was done. The lines could have been constructed by extending a rope between two posts and then removing the outer oxidized layer of surface rocks along the rope. The contrast of the red desert pebbles and the lighter earth beneath make the lines visible.
Due to this relatively easy method, rainfall would have easily eroded the drawings, but the dry desert environment has preserved the lines for hundreds and hundreds of years.
Most of the desert Nazca lines are only visible from the air. But some of the tracks were drawn on the hillside so you can see them from the ground as well.
To be more specific, the scale of the Nazca lines is HUGE! Some of the lines can be the size of a sports field. These designs were created over a long period, and in some cases, other lines overlapped the previous ones. That shows a lack of unification and long-term planning.